Inteligencia Artificial
Los planes estratégicos a menudo se crean en entornos acotados a la dirección y pasan a relegarse por la presión de las necesidades diarias y tendencias de mercado hasta que comienza el siguiente ciclo de planificación.
La estrategia crea un entendimiento común de lo que la organización quiere lograr y lo que necesita hacer para ello. Los planes estratégicos acortan la distancia entre esa aspiración y los proyectos específicos y las acciones diarias que, en última instancia como suma de todos ellos, responden a la estrategia.
La ejecución de los planes estratégicos suele conllevar demasiado tiempo y tiene un coste asociado superior a lo previsto originalmente. De hecho, sólo el 8% de los líderes estratégicos informan una tasa de éxito del 90% o superior en las iniciativas estratégicas a largo plazo.
Un plan estratégico bien definido se traslada la estrategia empresarial en iniciativas y acciones específicas que generan una hoja de ruta clara para ejecutarse y cumplir los objetivos comerciales.
Mediante el uso de herramientas y plantillas simples, los líderes funcionales pueden mapear y comunicar sus prioridades en una página o dos y hacer que sea más fácil para todos entender por qué y cómo ejecutar el plan a todos los miembros de los equipos acorde con las funciones de los mismos.
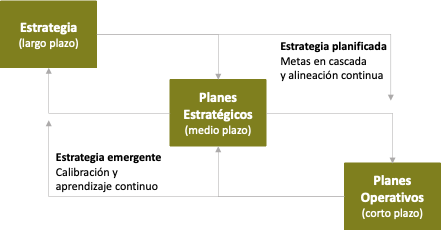
La planificación estratégica suele ser de cuatro tipos de y los tres niveles. Suele empezar a nivel organización, para luego convertirse en acciones.
Los tres niveles de planificación estratégica generalmente se refieren a la unidad de negocio frente a la corporativa y funcional. Los cuatro tipos de planes suelen ser estratégicos, operativos, tácticos y de contingencia.
Para ello hay que tener cuenta tres facrores esenciales cuando se realiza el plan: ambición, situación y capacidad adaptativa.
Ambición
Lo primero establecer un vínculo claro entre la estrategia y el plan.
Es fácil confundir la esencia de la estrategia con un plan estratégico detallado, especialmente cuando las condiciones cambian rápidamente y el horizonte del cambio es corto, pero la tarea número uno es conocer la diferencia y por qué es importante.
- La estrategia define la dirección a largo plazo de la organización, articulando lo que hará para competir y tener éxito en los mercados elegidos o lograr su misión.
- Los planes estratégicos definen cómo se llevarán a cabo sus ambiciones a largo plazo. Los planes estratégicos funcionales definen la hoja de ruta de iniciativas y la cartera de inversiones necesarias para lograr esos objetivos. En ellos, los líderes funcionales documentan las opciones y acciones necesarias para que la función cumpla con su contribución al modelo y los objetivos.
- Los planes operativos abordan la ejecución de proyectos y cambios específicos, así como cualquier tarea operativa que no esté incluida en el plan.
Esto significa crear marcos estratégicos centrados solo en lo material. Haciendo foco en supuestos críticos, métricas relevantes y las iniciativas clave que cada función necesita para contribuir de manera efectiva a los objetivos de la organización, incluso cuando estos cambian.
Situación
Analizar las tendencias clave y los factores cambiantes del mercado.
Es fundamental analizar y responder a las tendencias que podrían afectar la estrategia y por tanto el plan, y para las que es necesario realizar y prever suposiciones estratégicas de trabajo.
Ignorar o devaluar estos factores de distorsión o discontinuidad, a corto o largo plazo, produce vacíos críticos en el proceso de planificación, así como un gran coste de oportunidad, ya que pasa por alto las amenazas y las nuevas oportunidades para la propuesta de valor y el posicionamiento competitivo.
Diferentes encuentas ponen de manifiesto que en una horquilla alrededor de sólo el 38% de las organizaciones tienen un proceso formal para este tipo de detección de tendencias. En otro artículo de este blog se especifican los siete ámbitos clave de las tendencias que producen el cambio y para reforzar la naturaleza interconectada de estos factores (TPESTRE).
Cualquier responsable de quipos equipos pueden usar este modelo TPESTRE para identificar tendencias clave para construir suposiciones estratégicas a medida que comienzan a mapear qué acciones podrían ser necesarias en términos de modelos de negocio, personas, sus capacidades y sistemas de información.
Capacidad Adaptativa
Cuanto más rápidos seas los cambios en las condiciones operativas y situación del mercado que se requieren integrar en la estrategia a largo plazo, más adaptables deben ser los modelos de estrategia.
Un enfoque de estrategia adaptativa es lo que garantiza que la organización pueda detectar nuevas oportunidades antes y responder más rápidamente que sus competidores, lo que aumen¡ta las probabilidades de tener en un mundo con incertidumbres y cambios dinámicos.
Un enfoque de este estilo se basa en cuatro prácticadiseñadas para cambiar a la empresa desde un proceso rígido, de arriba hacia abajo, basado en el calendario, a un enfoque de estrategia más acore con los cambios e impulsado por eventos.
- Empezar la ejecución lo antes posible.
- Responder a los cambios a medida que se van produciendo.
- Acercarse y explorar las incertidumbres.
- Involucrar a toda la organización, clientes y terceros en la estrategia.
Otros factores clave
Un plan estratégico eficaz ayuda a los líderes de la organización a mejorar el enfoque y su capacidad de respuesta ante las actividades de planificación críticas para lograr los objetivos a largo plazo. Además permite, ante una visión global establecer los marcos adecuados para enfocar a los equipos en las cuestiones de mayor criticidad.
Para construir un plan que asegure el éxitoso con un proceso sólido y secuencial, los líderes funcionales deben:
- Garantizar el uso coherente de términos para minimizar la confusión en la planificación estratégica y establecer una línea de base para la colaboración.
- Construir una base sólida para una planificación más detallada estableciendo o probando la misión, la visión y la declaración de objetivos antes de iniciar la ejecución.
- Agilizar las aportaciones de las partes interesadas limitando la misión, la visión y el establecimiento de metas a la alta dirección, y dejando el desarrollo de objetivos, planes de acción, medidas y métricas a los gerentes con experiencia en ejecución.
Toda organización tiene unos aspectos clave que deben respetarse se en momento de la creación del plan y las actividades asociadas: Misión, Visión, Metas, Objetivos, Plan de acción y Medidas o métricas.
Cabe destacar dos aspectos de los mencionados anteriormente. El plan de acción estratégico que es un documento formal y fuente principal de información sobre cómo se ejecutarán, monitorearán, controlarán y cerrarán los objetivos. En ocasiones las organizaciones también incluyen un «plan de acción» asociado pero separado para lograr el modelo operativo.
Por otro lado las medidas son resultados observables que permiten evaluar la eficacia de los planes de acción. Las métricas cuantifican los cambios observados para permitir cuantificar objetivamente el progreso y alineamiento con las medidas elegidas.

