Crises create challenges in the face of current activity and scarce resources. At the same time activate the creativity and agile adoption of new relationship, work and business models to create value.
Research, Development and Innovation will be reinforced in the face of the opportunity of new behaviors and habits in the market. For this reason it allows Align current and innovation agendas to create more efficient and effective products and services.
To achieve this goal it is required:
- Evangelizar the entities' values and determine the best way to satisfy the service customer's needs thanks to focused, diverse and balanced work groups.
- Take advantage of the opportunities in the short and long term to realign and adapt to new priorities and business strategies.
- Ensuring resilience by evolving practices, processes and mindsets to accelerate business market response and foster agility in a volatile market.
- Use the current sense of urgency as acceleration force promoting shared intelligence through collaboration and knowledge ecosystems.
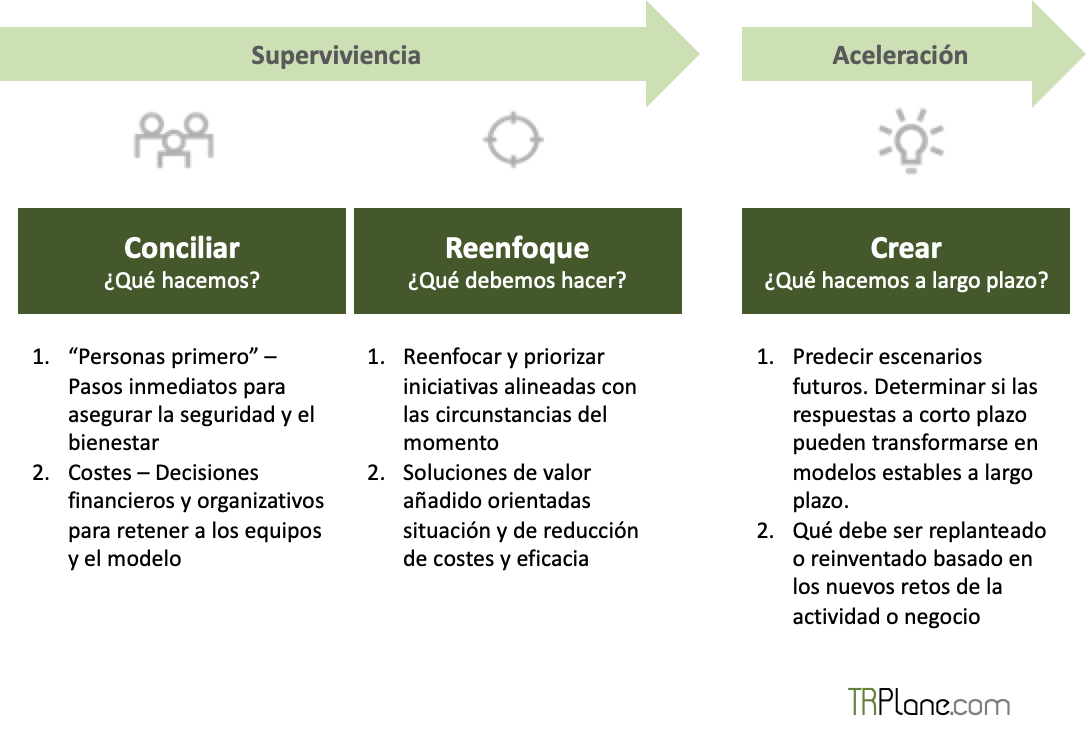
Three stages to identify change
In order to identify the innovation initiatives and the resulting change, it is necessary to establish some stages and ensure compliance with them that result in a complete plan with principles aligned with the entity's strategy.
In a first stage, work scenarios derived from people's new habits and market trends are identified, along with all possible routes and results. After this stage, they are aligned with the strategy and work agendas to experiment with probable results, either in the short term with incremental R&D&i or a more disruptive and long-term innovation.
Organizations must ensure their resilience by recognizing and planning for each stage of the crisis response. Opposite of being stuck in a stage in a cyclical way or in forward flight mode.
Some of these easily recognizable bad practices are:
- Investments in technology without accompanying internal culture, change management, customer needs, …
- Product launches that do not respond to customer needs
- Simulation or copying of products or services of leading companies in the market, without taking into account the learning process of said leaders to create best practices
In short, these stages include moving past survival, recognizing what will be needed in the response and recovery stages, and ultimately accelerating good practice by aligning, reinventing, or renovating the future.
Organizations that not only survive but they thrive, have the ability to fluidly change their plans based on users, consumers, market, society and politics. This supposes facility to assume the continuous change and the consequent alignment of strategies, goals and programs.
Key: Diverse and balanced Work Groups
Innovation can be neither a tactical plan that concludes with "we need to innovate" nor a strategy based on an annual budget model or a large consulting project financed every three or four years.
The people of the organization know their reality in all the perspectives and the challenges that appear. Faced with a pyramidal structure, by competencies, to effectively and efficiently address changes, Working Groups must be created that bring together all the necessary knowledge for each initiative.
The function of these Groups is to create new strategies or revise the existing ones aligned with the new habits and abilities of the people.
Their characteristics are:
- They include members with visibility into people's capabilities, are empathic, open-minded and creative.
- They reassess the relevance and priority of all strategic initiatives, whether current or planned.
- With the person at the center and understanding the changes in their behavior and seeking to add value aligned with the business.
These Working Groups they have access to market conditions, behaviors and short-term continuity solutions, and the long-term impacts of all of them on axes and growth.
A relevant initial function of the members of these groups is the evangelism. The culture of innovation and its extension in the organization is critical to create continuous value and the consequent growth.
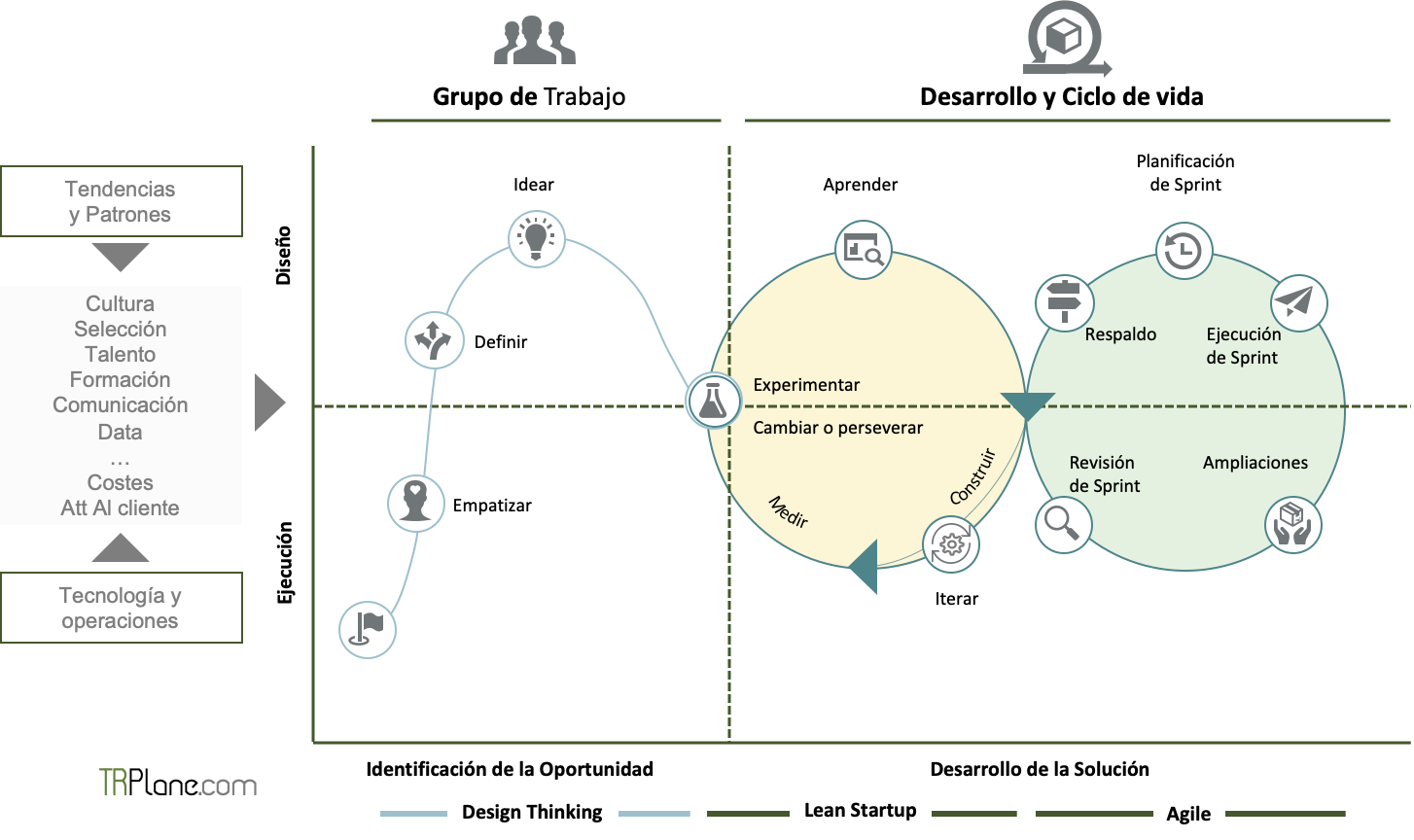
Innovation life cycle
History shows that consumers and businesses are looking for more profitable, faster and more creative products and services as they emerge from recessions.
Scarcity and limitations create urgency, focus, and increased creativity. Economic downturns and pandemics have been catalysts for the disruption of industries and the creation of new innovations.
| The 2008 financial crisis led to reduced incomes and a need for cheaper housing and transportation, giving rise to the innovation of a sharing economy. Sharing empty rooms and car rides led to successful disruptive startups like Uber, Airbnb y Groupon. Alibaba re-emerged with the SARS epidemic becoming one of the largest e-commerce companies in the world. During SARS, with retailers closed, employees telecommuting, and businesspeople around the world restricted in travel, Alibaba became the primary source for connecting American buyers with Chinese suppliers. |
For this reason in uncertainty it is necessary to change and evolve the portfolio of R+D+i with strengths and new capabilities and establish new performance objectives and goals.
For this you have to reassess and develop new processes and mindsets simplifying existing ones, avoiding over-collaboration and flattening structures. At the same time, communication must be encouraged to flow naturally in all areas of the organization.
current practices ideation, development and start-up of products and services must evolve reducing perfection to test the value proposition saving time and money in learning and pivoting towards the final model.
Customer value need not be tied to something shiny new like a new technology; instead, it can be linked to improving what already exists.
| Groupon he started by emailing coupons to his initial customers in test mode. There was no perfect logo, no perfect user interface, and no perfect database. But it quickly demonstrated a concept, gained traction, and then pivoted and evolved into the solution you have today. |
In the new reality derived from the crisis, the team's resources are evaluated, based on the changes in the business, the innovation strategies and the innovation portfolio.
It may be necessary, for example, to bring in additional innovation team members from business areas to support real-time discussions about changes in customer behavior.
| Most organizations were quick to adopt remote work, and innovation labs were quick to move along that line. Teams created virtual Kanban boards to replace whiteboards and online workshops appeared, keying all collaboration to virtual rooms. |
Another criterion to take into account in the innovation cycle is the adopting a connect-the-dots approach recreating, improving, or expanding on existing ideas or solutions, rather than reinventing the wheel or doing the same thing with just cosmetic changes.
For this, it is a good practice to research across industries, including other sectors, countries and other business models.
| Howard Schultz, founder of Starbucks, was mesmerized by the way Europeans gathered in coffee shops and recreated the concept in America as Starbucks. McDonald's took the popular burger experience and just made it faster. |
Taking all these factors into account, it is necessary to promote an innovation model that is sufficiently flexible, fast, and that is in constant review and learning in each initiative.
Other relevant examples resulting from applying these principles
| Mailchimp: automating what already exists. Mailchimp was a design consulting company whose clients wanted email newsletters. They built a tool that would streamline the process that is now widely used by users around the world in subscription mode. Lynda.com: automating what already exists. A teacher in the late 90's started producing training videos for her students. The same company helped software developers improve their skills. It was acquired by LinkedIn for $1.5 billion. Shopify: Improved value in the existing business model. The founders were looking for a shopping cart solution for a snowboard ecommerce. Unable to find one that met their needs, they created a custom solution that turned out to be the perfect fit for many businesses. |
Do you have more examples? Are any of these concepts and keys applied in your company? Do you have samples of innovation focus errors? share them





