The environmental, social and corporate governance (ESG, Environmental, Social & Governance) aspects are an evaluation of the collective awareness of a company regarding the social and environmental factors that can or should have an impact, either due to personal motivation or needs. regulatory.
It is typically a score that is constructed from data collected around specific metrics related to intangible assets within the company. It could be considered a form of corporate social credit valuation.
Analysis shows that these intangible assets comprise an increasing percentage of the organization's future business value. While there are many ways of thinking and things to consider in intangible asset metrics, these three core factors together, ESG, comprise a label that has been adopted across the industry.
They are used for a wide variety of specific purposes with the ultimate goal of measuring elements related to the sustainability and social impact of a company or business.
In less than 20 years, the ESG movement has grown from a corporate social responsibility initiative launched by the United Nations to a global phenomenon representing more than $30 trillion in assets under management. In 2020 last year, a total of $17,67 billion in capital raising was diverted into ESG-linked products, an increase of nearly 525 percent from 2015, according to Morningstar.
It is not a fashion. It can be associated with environmental problems such as climate change or waste, fossil fuels. the scarcity of resources, among others, but it also reaches a social level such as human resource management, DEI (Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion), safety, well-being, health...) and corporate governance criteria.
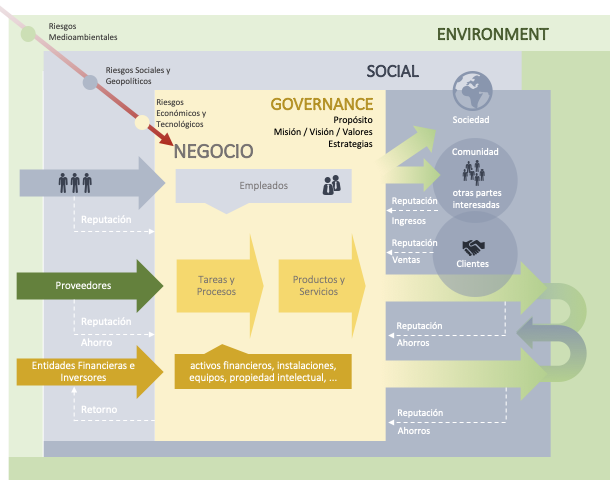
Functional Scheme of the ESG Approach
To apply an ESG model, a system is required to feed the initiatives, maintain them, and progressively monitor their results.
The direct and indirect impacts of the company on key stakeholders (employees, the environment, society in general, communities and customers) are quantified and connected to where and how those impacts occur in the business model .
Key aspects of an ESG management application
Managing ESG initiatives from a centralized application, updated not only in the progress of the initiatives, but also in regulatory, legal and compliance market information, allows knowing the results and benefits at all times.
- Integration with external data sources, at the level of assets, transactional, analytical, and with defined capture cadences, either every day or every 15 seconds for maximum control.
- Reliable reports whether full or partial from stakeholders you may need, including reporting to DJSI, CDP, SASB and UNGP. All metrics in one place.
- Normative compliance with access to consistently updated global regulatory information, including GRI content, reducing the time and effort required to assess changes in regulatory content against compliance requirements. Minimize the cost of compliance processes.
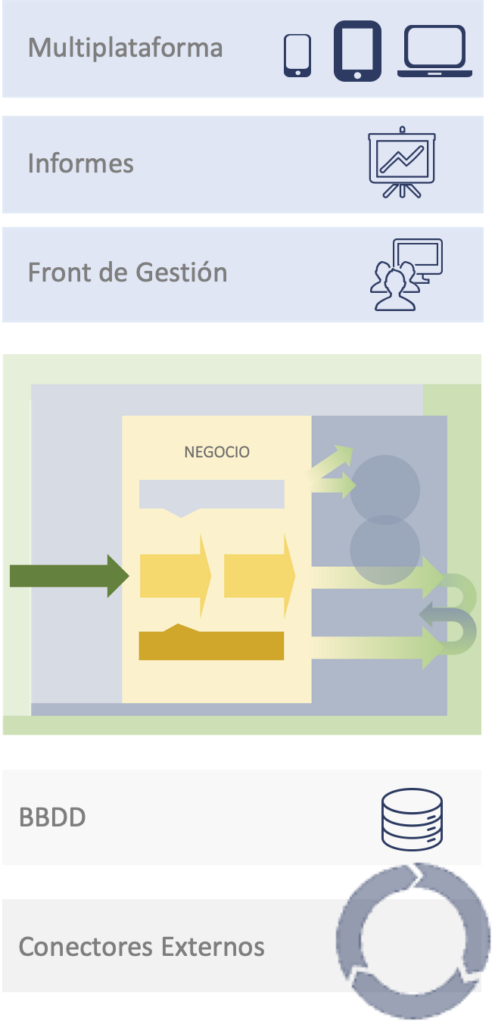
- Maximum operational impact with a vision of sustainability and the environment. Quality and supplier management.
- Regulatory safeguard allowing issues to be addressed before they become violations or fines with triggers based on regulatory thresholds. Cost reduction in external audits.
- Reduce input and calculation errors for all data entry while managing version control when variables such as emission factors change over time for maximum accuracy.
- Holistic sustainability vision with sustainability initiatives with multi-level tasking capabilities, calculating ROI for initiatives and performance tracking.
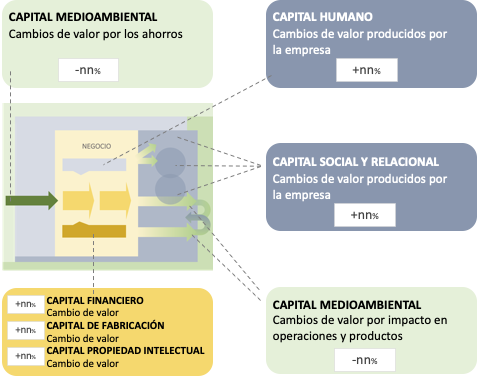
ESG Dashboard
The main result of an ESG system provides an overview for decision-making of the financial and non-financial performance of the company, at an aggregate level, by initiative, and with different verified numerical metrics.
In an aggregate vision, the results can be grouped according to the type of capital they produce for the company, either as profit or as savings.
Key features of an ESG solution
When choosing an ESG solution, it is necessary to ensure a series of characteristics that facilitate its implementation and subsequent maintenance.
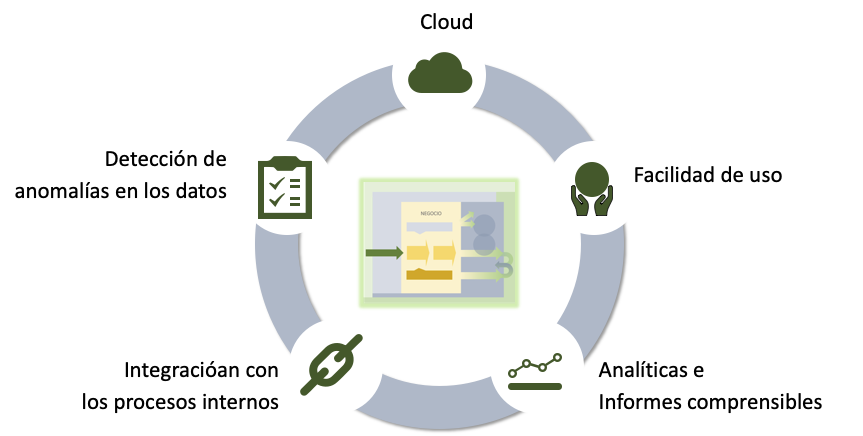
In the Cloud aspect, it must be ensured that it supports multi-platform and is accessible from a mobile phone for agile monitoring.
Having easy-to-use software means not finding bureaucratic limits or burdens on people's tasks, therefore costs and change management are reduced.
The results must be understandable, analysable, and allow unambiguous decision-making, since they can be understood by everyone.
Most of the organization's initiatives, operations, and transactions are found in a vast number of enterprise solutions. Having the ability to integrate with ESG data makes it easier to maintain and view the return of ESG strategies.
One of the main problems of organizations are errors or anomalies in the data, either because they do not have a data strategy, either due to operational errors or the systems themselves. Being able to have alarms or controls on the data avoids distortions in the processes derived from its analysis.
In conclusion, meeting ESG criteria improves returns, and a well-managed and responsible company that cares about people, its customers, society and the environment has a better perception by the market and against the competition.





